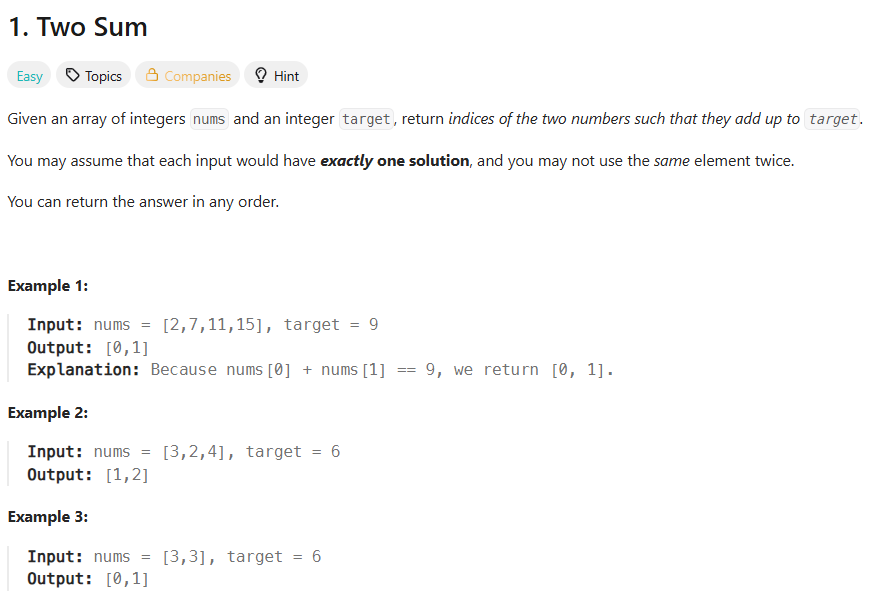
Easy | Leetcode 1. Two Sum
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
LeetCode link: 點此進入LeetCode
NeetCode link: 點此進入NeetCode
Easy | Leetcode 1. Two Sum
Question
給你一個整數陣列 nums 和一個整數 target,請你找出陣列中兩個數字,使它們的和等於 target,並回傳這兩個數字的索引。 假設每種輸入只會對應一個答案,而且同一個元素不能重複使用。
Solution
Solution1: Brute Force
解題概念:
使用兩層 for 迴圈,把所有可能的兩個元素加起來一一嘗試是否等於 target。
程式碼:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Solution1 {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 外層迴圈:從第0個元素開始
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 內層迴圈:從第 i+1 個開始,避免重複與自己相加
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
// 檢查兩數之和是否等於目標值
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[] {i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[]{};
}
}
複雜度分析:
- Time complexity: $O(n^2)$
- 外層跑 n 次,內層平均跑 (n-1)/2 次,所以是平方級時間。
- Space complexity: $O(n + m)$
- 沒有使用額外資料結構(只回傳答案),空間複雜度為常數等級。
- 沒有使用額外資料結構(只回傳答案),空間複雜度為常數等級。
Solution2: Sorting
解題概念:
- 把 nums 轉成一個 2D 陣列 A,每個元素為 [值, 原本的 index]。
- 接著排序這個 A,根據 值 來排。
- 用雙指針:j 指向最小值、k 指向最大值,檢查兩數和是否為 target。
- 若和太小,左邊往右;若和太大,右邊往左;接著重複檢查。
程式碼:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class Solution2 {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 將 nums 陣列轉換為二維陣列
int[][] A = new int[nums.length][2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
A[i][0] = nums[i]; // 元素0: 數值
A[i][1] = i; // 元素1: 索引
}
// 根據值進行排序
Arrays.sort(A, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
// 利用雙指針,最左到最右加起來檢查是否 = target
int j = 0, k = nums.length - 1;
while(j < k) {
int sum = A[j][0] + A[k][0];
if (sum == target) {
// 回傳原本的索引:記得小的放前,大的放後!!
return new int[]{Math.min(A[j][1], A[k][1]),
Math.max(A[j][1], A[k][1])};
}
else if (sum < target) {
// 總和過小,左指針向右(讓總和變大)
j++;
}
else {
// 總和過大,右指針向左(讓總和變小)
k--;
}
}
return new int[]{};
}
}
複雜度分析:
- Time complexity: $O(log n)$
- 建立 2D 陣列:$O(n)$
- 排序:$O(n log n)$
- 雙指針搜尋:$O(n)$
- Space complexity: $O(n)$
- 額外使用一個 int[n][2] 來記錄數值和索引 → $O(n)$。
- 額外使用一個 int[n][2] 來記錄數值和索引 → $O(n)$。
Solution3: HashMap (Two pass)
解題概念:
- 我們使用一個 Map<Integer, Integer>(值 → 索引)來記錄每個數字出現的位置。
- 對於每個數字 nums[j],我們都想找出「另一個數 diff = target - nums[j]」是否已經出現過。
- 如果存在這個數,且它的 index 不等於 j(不能自己加自己=target),那就是答案。
程式碼:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public class Solution3 {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 建立 Map:儲存每個數值對應的索引
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 先把所有數值及其索引放進 map 中
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
// 再次遍歷陣列,尋找是否存在配對值
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
int diff = target - nums[j]; // 所需的配對數字
// 檢查 map 中是否有這個數,且不是自己
if (map.containsKey(diff) && map.get(diff) != j) {
return new int[]{j, map.get(diff)};
}
}
return new int[]{};
}
}
複雜度分析:
- Time complexity: $O(n)$
- 第一次迴圈:把 nums 所有值加進 map → $O(n)$
- 第二次迴圈:查找是否有符合的配對 → 每次查找 $O(1)$,總共 $O(n)$
- Space complexity: $O(n)$
- map 需要存放最多 n 個 key-value pair(數值與其 index)。
- map 需要存放最多 n 個 key-value pair(數值與其 index)。
Solution4: HashMap (One pass)
解題概念:
這個解法將「查找」與「記錄」結合在同一個迴圈中完成:
- 對每個數 nums[i],我們計算與它搭配會變成 target 的數字 diff = target - nums[i]。
- 我們在遍歷時就「邊走邊查」,看 diff 是否已經存在於 HashMap 中。
- 如果有,那就表示我們之前遇過的某個數字可以和現在的 nums[i] 配對起來等於 target。
- 如果沒有,就把現在這個數字和索引記錄起來(以備之後使用)。
程式碼:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class Solution4 {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 建立 Map:儲存每個數值對應的索引
Map<Integer, Integer> prev_map = new HashMap<>();
// 一次迴圈就完成:查找 + 記錄
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int diff = target - nums[i];
// 如果 map 中已經有這個補數,表示找到一組解
if (prev_map.containsKey(diff)) {
return new int[]{prev_map.get(diff), i};
}
// 如果沒有,就記錄目前這個數和它的 index
prev_map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[]{};
}
}
複雜度分析:
- Time complexity: $O(n)$
- 只走一次迴圈,每次都做一次查詢與插入(HashMap 這兩項都是 $O(1)$)。
- Space complexity: $O(n)$
- 最壞情況下 HashMap 要存放 n 個元素(每個數字與其索引)。
本文章以 CC BY 4.0 授權